Explain How Preoperational Thought Differs From Sensorimotor Thought
The preoperational stage is the second stage in Piagets theory of cognitive development. Explain how preoperational thought differs from sensorimotor thought.
Ages 7 to 11.

. The sensorimotor stage is the first stage of your childs life according to Jean Piagets theory of child development. Want to see the full answer. This stage begins around age 2 as children start to talk and lasts until approximately age 7.
The preoperational stage is the second stage in Piagets cognitive developmental theory occurring between 2 and 7 years of age. The sensorimotor stage birth to two years the preoperational stage two to seven years the concrete operational stage seven to eleven years and the formal operational stage. Birth to 2 years.
The preoperational stage is the second stage in Piagets theory of cognitive development. This stage begins around age two and lasts until approximately age seven. Check out a sample QA here.
A childs arms might become airplane wings as she zooms around the room or a. During this stage children begin to engage in symbolic play and learn to manipulate symbols. If you have ever had responsibility for children.
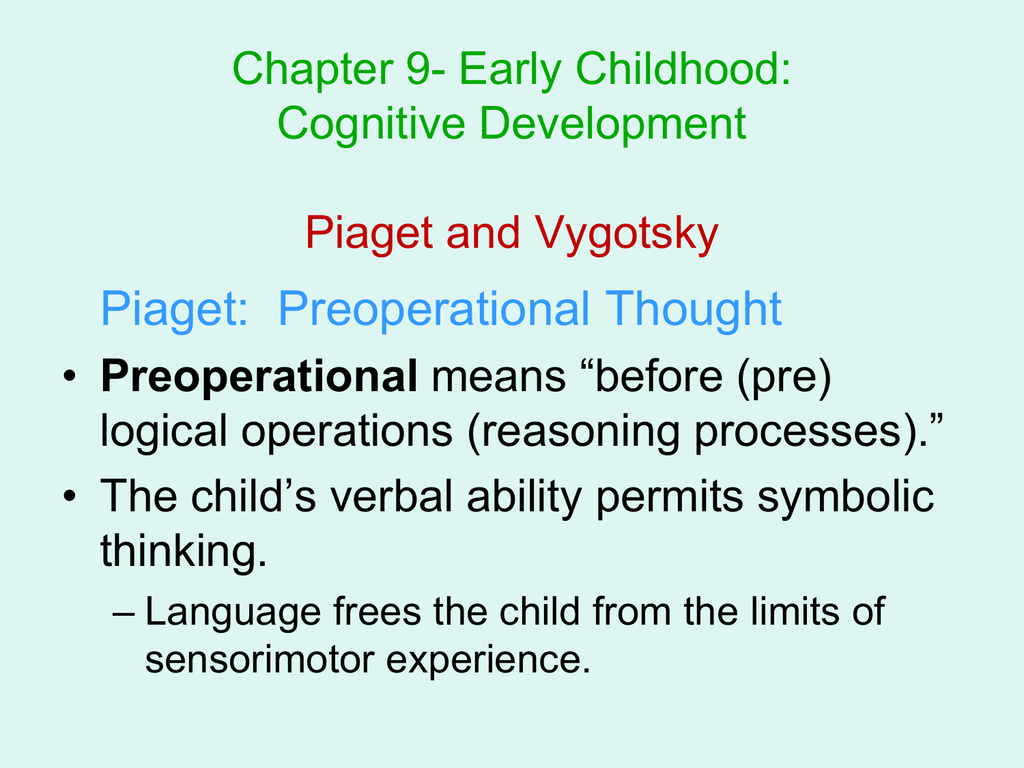
Preoperational Thought Pre-Operational Thought In Piagets theory of cognitive development the second stage is called Preoperational Thought. The childs thinking during this stage is pre before operations. They are mentally thought out rather than done physically.
The first stage of cognitive development is sensorimotor stage. Describe the concepts of the zone of proximal. 1 Piagets stages are.
Ages 12 and up. They was nt much hesitation. I expect thorough well-thought out answers for each question.
It begins at birth. Start your trial now. Piagets second stage of cognitive development is called the preoperational stage and coincides with ages 2-7 following the sensorimotor stage.
In the preoperational stage children use symbols to represent words images and ideas which is why children in this stage engage in pretend play. Pre operational stage is between 2-4 years of age when the toddler can hold and feel objects but cant necessarily manipulate them. Explain how preoperational thought differs from sensorimotor thought.
And explain how this information could be used by parents and teachers. This problem has been solved. Learning is active and there is no conceptual or reflective thought.
According to Piaget this stage occurs from the age of 2 to 7 years. Age 2 to 7. Ages 2 to 7.
During this period children are thinking at a symbolic level but are not yet using cognitive operations. Piagets stage that coincides with early childhood is the Preoperational Stage. Explain Banduras Social Cognitive Theory and how it is different from Piagets Cognitive-Developmental Theory.
The sensorimotor stage differs from the preoperational stage in that in the preoperational stage the child is using symbolic thinking consistently and has a lot of imagination while in the sensorimotor stage the child learns about the world through movements and sensations. Explain how preoperational thought differs from sensorimotor thought. Their whole view of the world may shift.
When they zoom around. During the preoperational stage many of the childs existing schemas will be challenged expanded and rearranged. 5pts 5 Describe physical growth and changes in gross and fine motor skills during middle and late childhood.
During this stage which occurs from 4-7 the child begins to go beyond recognizing and is able to use words and images to refer to objects. Piaget explains operations as thought out actions. 5pts 4 Explain what Erikson means by saying that early childhood is dominated by feelings of initiative versus guilt.
Make sure to number your answers to the questions accordingly and proofread before submitting. Preoperational thought includes language and imagination which involve symbolic thought but not yet logical operational thinking. Describe the 4 stages of Piagets Cognitive Development Theory from Sensorimotor Preoperational Concrete Operational and Formal Operational.
In the sensorimotor stage if and infant thought about it they did it. One of the most obvious examples of this kind of cognition is dramatic play or the improvised make-believe of preschool children. His theory focuses not only on understanding how children acquire knowledge but also on understanding the nature of intelligence.
However Piaget noted that they do not yet understand. What does Piaget mean by operations. For example around the age of 2 a child starts to refer to specific toys as doll or bear or even have.
Explain how preoperational thought differs from sensorimotor thought. Preoperational Stage Definition. First week only 499.
Now in the preoperational stage children can reconstruct their behavior and think before they do something. According to Rardin and Moan 1971 there are four stages in childrens cognitive development that are formulated by Piaget namely the sensorimotor preoperational concrete operational and lastly formal operational refer to Figure 1 in Appendix 1. During these years a child begins.
As your child moves from the sensorimotor stage the first of Piagets cognitive development stages to the preoperational stage youll notice their imagination developing. Sensorimotor thought infants use senses and motor abilities to understand the world. Sensori-motor stage of development is the first stage of development during the infant years - 1- 2 years of age the child can use the sense of touch to feel objects and their effects.
In the preoperational stage children use their new ability to represent objects in a wide variety of activities but they do not yet do it in ways that are organized or fully logical.

Piaget S 4 Stages Of Cognitive Development Explained Child Development Theories Child Development Psychology Cognitive Development

31 Describe Piaget S Theory Of Intellectual Development With Special Regard To The Following Assimilation And Acc Development Piaget Theory Object Permanence

Cognitive Development Psychology Notes Cognitive Development Piaget Theory

Piaget S Cognitive Development Theory Cognitive Development Child Development Theories Child Development Teaching

31 Describe Piaget S Theory Of Intellectual Development With Special Regard To The Following Assimilation And Ac Piaget Theory Theories Cognitive Development

What Are Piaget S Four Stages Of Development The Sensory Toolbox

What Is The Sensorimotor Stage Of Cognitive Development Cognitive Development Stages Of Baby Development Development

What Is The Sensorimotor Stage Of Development Edugage

According To Psychologist Jean Piaget Children Progress Through A Series Of Four Critical Child Development Theories Jean Piaget Child Development Activities
Stages Of Cognitive Development Jean Piaget

Jean Piaget Theory Of Cognitive Piaget Stages Of Development Jean Piaget Child Development Psychology

Pin On Christian Counseling For Mental Health Issues

The Jean Piaget Stages Of Cognitive Development The Psychology Notes Headquarters

Jean Piaget Cognitive Theory Simply Psychology Piaget Stages Of Development Psychology Notes Nursing Classes

Piaget S Stages Of Cognitive Development The 4 Stages Of Development




Comments
Post a Comment